Abstract
Background: Bortezomib or lenalidomide, in combination with dexamethasone, have been the dominant treatment options for multiple myeloma (MM) over the past decade, both in the frontline and later lines of treatment. Little evidence exists regarding how survival outcomes associated with each of these treatment modalities in a clinical trial (CT) setting compare with those observed in a real-world (RW) setting.
Objectives: To compare OS outcome of relapsed refractory MM patients receiving lenalidomide+dexamethasone (Rd) or bortezomib+dexamethasone (Vd) in the RW versus CT settings.
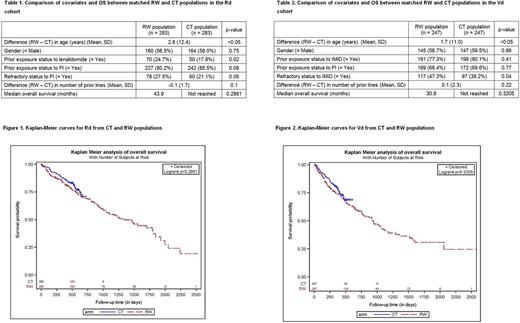
Methods: Patients in two RW data sources - SEER-Medicare and Optum™ integrated databases 1) with an index ICD-9 diagnosis code for MM any time from January 1, 2007 until December 31, 2013, 2) aged ≥ 18 years and 3) with no concurrent primary cancers or previous diagnosis of cancer during the 365-day lookback period prior to index diagnosis were included in the study. Lines of treatment (LOTs) were identified based on business rules centered on continuity and concurrence of drug usage. CT data were sourced from the POLLUX trial (for Rd patients) and from the CASTOR trial (for Vd patients). In the post-frontline (i.e., LOT2+) setting, Rd (and Vd) patient instances in the RW population were matched with CT patients on the basis of covariates identified as significant predictors of OS in the respective cohorts. Rd patient instances were matched on the basis of age, gender, prior exposure status to lenalidomide, prior exposure status to a proteasome inhibitor (PI), refractory status to PI and number of prior lines of treatment. Vd patient instances were matched on the basis of age, gender, prior exposure status to an immunomodulatory drug (IMiD), prior exposure status to PI, refractory status to IMiD and number of prior lines of treatment. 1:1 matching was achieved for the CT cohorts from among the RW cohorts. The covariates used for matching and OS of the Rd and Vd cohorts were compared between the RW and CT populations after matching.
Results: The size of the RW cohorts used for matching were 789 and 722 for Rd and Vd, respectively; the size of the corresponding CT cohorts were 283 and 247. In the matched Rd cohort (n=566), prior exposure status to lenalidomide and age were significantly different (p<0.05) between the RW and CT populations (Table 1). In the Vd matched cohort (n=494), refractory status to IMiD and age were significantly different (p<0.05) between the RW and CT populations (Table 2). For both of the treatment modalities, the RW and CT populations had similar OS (HR = 1.26, 95% CI = 0.86-1.84 in Rd (Figure 1), and HR = 1.19, 95% CI = 0.84-1.70 in Vd (Figure 2)).
Conclusions: In this matched analysis,the outcomes in relapsed refractory MM patients receiving Rd or Vd in the RW setting were similar to those of the CT patients. The benefit of adding a third agent observed in the CT setting may apply to the RW setting as well.
Nooka: Amgen, Novartis, Spectrum, Adaptive tecnologies: Consultancy. Voorhees: Oncopeptides: Consultancy; Amgen: Speakers Bureau; Celgene: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Takeda: Consultancy; Bristol-Myers Squibb: Consultancy; Janssen: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Novartis: Consultancy. Kumar: Skyline: Honoraria; Celgene, Millennium, BMS, Onyx, Janssen, Noxxon, AbbVie, Amgen, Merck, Oncopeptides, Skyline Diagnostics, Takeda: Consultancy; Celgene, Millennium/Takeda, Onyx, AbbVie, Janssen, Sanofi, Novartis, Amgen, Genentech, Merck, Oncopeptides, Roche, Skyline Diagnostics: Research Funding. Mehra: Janssen: Employment. Lam: Janssen: Employment. Slavcev: Janssen: Employment. Potluri: SmartAnalyst Inc.: Employment; Janssen: Consultancy, Research Funding. Dasgupta: SmartAnalyst Inc.: Employment; Janssen: Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal